A healthy gut is vital for digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. If you’re wondering how to improve gut health, it’s essential to understand the habits that harm it and what you can do to restore a healthy balance. Certain lifestyles can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome, leading to issues like inflammation, poor digestion, and even mental health struggles. Here are five habits that can negatively impact gut health—and what you can do to improve and protect your gut health.
1. Alcohol Consumption

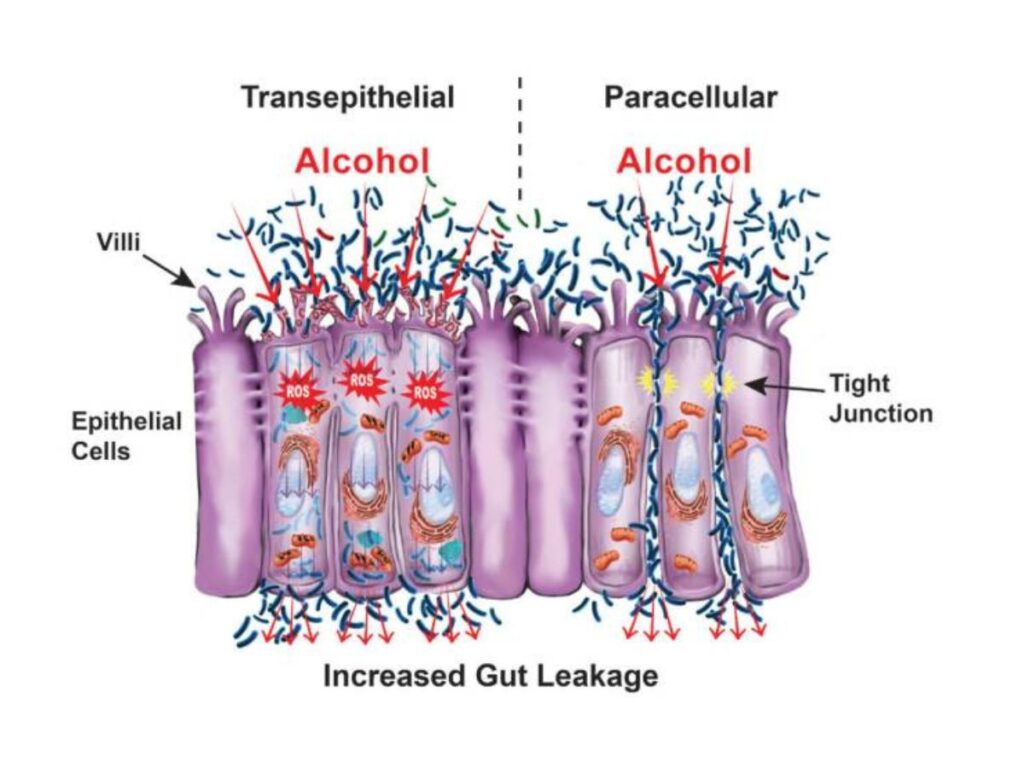
While social drinking, defined as two drinks per day, may not do immediate damage, excessive intake can damage the gut lining and alter the microbiome. Studies show that heavy drinking increases gut permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut,” allowing harmful substances to enter the bloodstream and triggering inflammation. Alcohol also reduces beneficial bacteria while promoting the growth of harmful microbes, leading to digestive distress and immune dysfunction.
How to Decrease Alcohol Intake:
To be clear, avoiding alcohol altogether is best for your health, as there is no completely safe limit when it comes to its effects. However, if you do choose to consume alcohol, try these tips to minimize its impact on gut health.
- Limit alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day for women and two for men.
- Opt for polyphenol-rich choices like red wine, which may have some gut-friendly properties.
- Drink plenty of water alongside alcohol to reduce its impact on the gut lining.
- Support your gut with prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kimchi, and asparagus.
2. Poor Sleep Disrupts Gut Health
Lack of sleep doesn’t just leave you feeling sluggish, it also disrupts your gut microbiome. Research suggests that sleep deprivation alters microbial diversity, increases inflammation, and weakens the gut barrier. Poor sleep quality has also been linked to metabolic disorders, weight gain, and increased susceptibility to gastrointestinal conditions.
Tips to Improve Sleep Hygiene:
- Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time daily.
- Reduce screen time before bed, as blue light interferes with melatonin production.
- If you’re taking a Vitamin D supplement, it may be beneficial to take earlier in the day to avoid interference with melatonin production
- Practice relaxation techniques such as singing bowl sound meditation, deep breathing, or reading before bed.
3. Chronic Stress Impairs Gut Health
Both acute and chronic stress can wreak havoc on the gut. Studies show stress affects the gut-brain axis, leading to changes in gut motility, increased gut permeability, and shifts in microbial composition. Chronic stress is also associated with visceral hypersensitivity and heightened inflammation, which can contribute to digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
How to Reduce Stress & Improve Gut Health:
- Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness meditation and yoga.
- Engage in regular physical activity, as exercise helps regulate gut microbiota.
- Prioritize self-care activities like journaling, spending time in nature, or connecting with loved ones.
- Try adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha or Rhodiola, which may help reduce stress levels.
4. Lack of Food Diversity Harms Your Gut

A diverse diet is essential for maintaining a thriving gut microbiome. Diets high in processed foods and low in fiber can lead to reduced microbial diversity and an imbalance in gut bacteria. Research indicates that diets lacking variety, especially those high in refined sugars and low in plant-based foods, can contribute to conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and metabolic disorders.
How to Increase Food Diversity & Improve Gut Health:
- Eat a wide range of whole foods, particularly fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
- Include fermented foods like kefir, kimchi, miso, and kombucha to support a healthy microbiome.
- Experiment with new foods each week to increase microbial diversity.
- Reduce ultra-processed foods and refined sugars, which can feed harmful bacteria.
5. Too Much Red Meat Is Bad For Gut Health
Red meat, particularly processed meats, can negatively impact gut health. Studies show that excessive consumption is linked to an increase in harmful gut bacteria, inflammation, and the production of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a compound associated with heart disease. A diet high in red meat and low in fiber may also contribute to gut dysbiosis, leading to increased risk of digestive issues like ulcerative colitis and an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
How to Reduce Meat Intake & Improve Gut Health:
- Limit red meat intake to less than 18 ounces weekly, choose lean cuts and grass-fed options.
- Balance your diet with plant-based protein sources like legumes, tofu, and quinoa.
- Increase fiber intake from vegetables, whole grains, and fruits to support gut bacteria.
- Avoid processed meats like sausages, hot dogs, and bacon altogether, which have been linked to gut inflammation and colorectal cancer.
Additional Tips on How to Improve Gut Health
Beyond avoiding these harmful habits, here are some additional ways to support gut health:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps maintain gut motility and overall digestion.
- Get Enough Fiber: Fiber-rich foods like organic oats, flaxseeds, and leafy greens feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity has been shown to positively influence gut microbiota composition.
- Prioritize Prebiotics: Foods like garlic, onions, and bananas contain prebiotic fibers that nourish good bacteria.
- Reduce Artificial Sweeteners: Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners can negatively alter gut bacteria balance.
Final Thoughts on Improving Gut Health
Your gut health plays a vital role in your overall well-being, affecting everything from digestion to mental clarity. By making mindful lifestyle changes: such as reducing or eliminating alcohol intake, prioritizing sleep, managing stress, diversifying your diet, you can cultivate a healthier gut and improve your overall health. Small changes today can lead to big benefits for your microbiome and overall health.
Struggling with gut health issues? Our expert gut health dietitians can help restore your gut health with personalized nutrition counseling, that’s covered by most insurance plans. Don’t let digestive issues disrupt your life—schedule your consultation today and start improving your gut health.

